Introduction:
In today's interconnected digital landscape, network security is paramount. One crucial tool in the arsenal of cybersecurity professionals is the Intrusion Detection System (IDS). This lab focuses on Snort, a powerful and widely used open-source IDS/IPS solution.
Snort is designed to monitor network traffic in real-time, analyzing packets for suspicious activity based on predefined rules. When potential threats are detected, Snort can generate alerts, log the activity, or even take preventive action, depending on its configuration.
In this lab, we will explore the fundamentals of Snort, including its basic operation, rule syntax, and various modes of operation. We'll start by running Snort in its default sniffer mode, then progress to using it as an intrusion detection system. We'll also examine how Snort processes packet capture (pcap) files and generates logs.
Lab Questions and Answers: 1.1 Core Concepts
1. An IDS/IPS can be used to:
(select all that apply)
A. Identify security vulnerabilities.
B. Detect suspicious activity.
C. Block suspicious activity.
D. Manage access controls for users.
Answer: B, C
2. IDS/IPS are typically integrated into:
(select all that apply)
A. Wireless access points
B. Firewalls
C. Vulnerability scanners
D. SIEMs
Answer: B
3. What are the three Snort modes?
(select all that apply)
A. Sniffer
B. Alerting
C. Logging
D. Inline
E. Intrusion Detection
Answer: A, C, E
4. Where does Snort keep its default configuration file (Snort.conf)?
Answer: /etc/Snort
Lab Questions and Answers: 1.2 Guided Exercise
1. What is the file path for the Snort rules file?
Answer: /etc/snort/rules/local.rules
2. What Snort command line option is used to select the interface that Snort listens on?
Answer: -i
Hint: Find from the help menu.
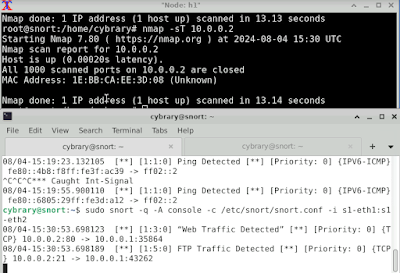
3. How many Snort alerts does your ping to 10.0.0.2 generate?
8
Hint: Count the total number of "Ping Detected" after ping.
4. After killing the python web server and executing wget http://10.0.0.2/index.html a second time, does Snort generate alerts?
A. Yes
B. No
Answer: A
Lab Questions and Answers: 1.3 Challenge Exercise
1. What was the first rule you needed to add to /etc/snort/rules/local.rules to have Snort alert "FTP Traffic Detected"?
Answer: alert tcp any any -> any 21 (msg:"FTP Traffic Detected"; sid:4;)
2. What was the second rule you needed to add to /etc/snort/rules/local.rules to have Snort alert "FTP Traffic Detected"?
Answer: alert tcp any 21 <> any any (msg:"FTP Traffic Detected"; sid:5;)
Conclusion:
This lab has provided a comprehensive introduction to Snort, one of the most popular open-source intrusion detection systems available. Through hands-on exercises, we've explored various aspects of Snort's functionality and capabilities.
We began by running Snort in its basic sniffer mode, observing real-time network traffic and understanding the wealth of information Snort can provide about packet flows. We then progressed to using Snort in its intrusion detection mode, leveraging its powerful rule-based system to identify potentially suspicious activities.
The lab also demonstrated Snort's versatility in analyzing both live traffic and pre-captured packet files (pcaps), showcasing its utility in both real-time monitoring and forensic analysis scenarios. We learned how to interpret Snort's alerts and logs, gaining insight into the types of threats an IDS can detect.